

Many processes are covered with a layer of lipid material called the myelin sheath. The axon conducts the impulses to the dendrite of another neuron or to an effector organ that is thereby stimulated to action.
#All or none principle of neural transmission skin#
The dendrites receive stimuli from other nerves or from a receptor organ, such as the skin or ear, and transmit them through the neuron to the axon. The multipolar neurons have a single process called an axon and several branched extensions called dendrites. Most neurons are multipolar this type is widely distributed throughout the central nervous system and autonomic ganglia. At the synapse, the firing of an action potential in one neuronthe presynaptic, or sending, neuroncauses the transmission of a signal to another neuronthe postsynaptic, or receiving, neuronmaking the postsynaptic neuron either more or less likely to fire its own action potential. How is a neuron firing similar to a toilet. Neurons communicate with other neurons, muscles or glands through the generation and conduction of nerve impulses. the principle that under given conditions the response of a nerve or muscle fiber to a stimulus at any strength above the threshold is the same: the muscle. The diagram below summarizes neural transmission within the nervous system.
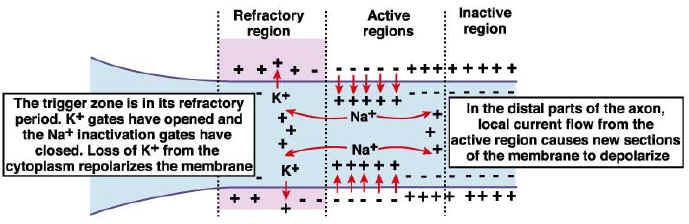
A neuron having two processes is bipolar, and one with three or more processes is multipolar. All-or-none principle Direction of impulse Refractory period Threshold Resting potential Action potential. Thus, the process follows an All or None principle, since the action potential does not rely on the triggering stimulus’ strength, but on the cell membrane’s permeability. A nerve cell may have only one such slender fiber extending from its body, in which case it is classified as unipolar. The nerve fibers are actually extensions of the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus of the neuron. There are no big or small action potentials in one nerve cell - all action potentials are the same size. They are composed of a cell body (called also neurosome or perikaryon), containing the nucleus and its surrounding cytoplasm, and one or more processes ( nerve fibers) extending from the body. When neurons undergo activation or firing (that is, sending out an electrical impulse), neural. In other words, neurons are centers of communication inside the nervous system. It is an electrically excitable cell that transfers information within the nervous system. All or none law: The nerve will either conduct the impulse along its entire length or will not conduct the impulse at all. A highly specialized cell of the nervous system, having two characteristic properties: irritability (ability to be stimulated) and conductivity (ability to conduct impulses). The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
